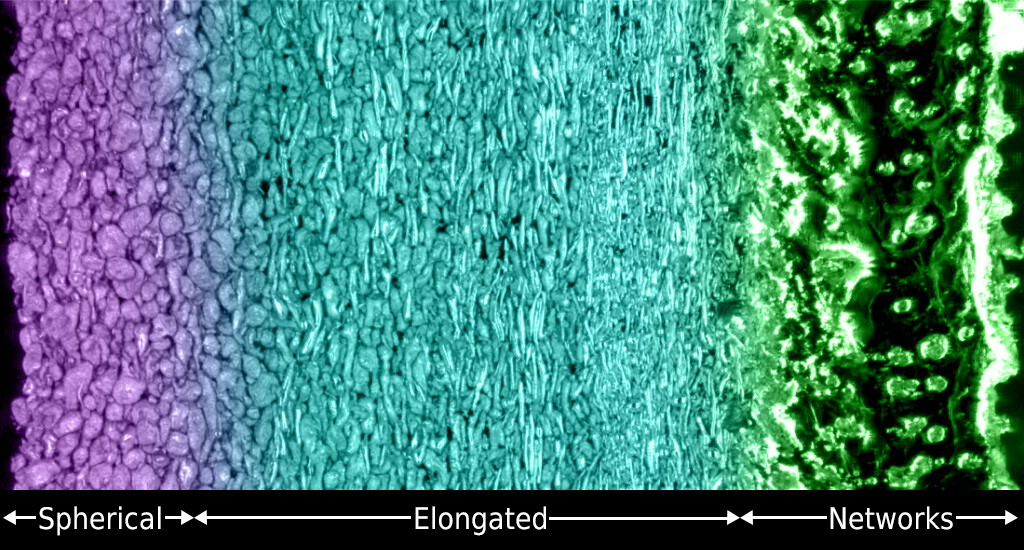
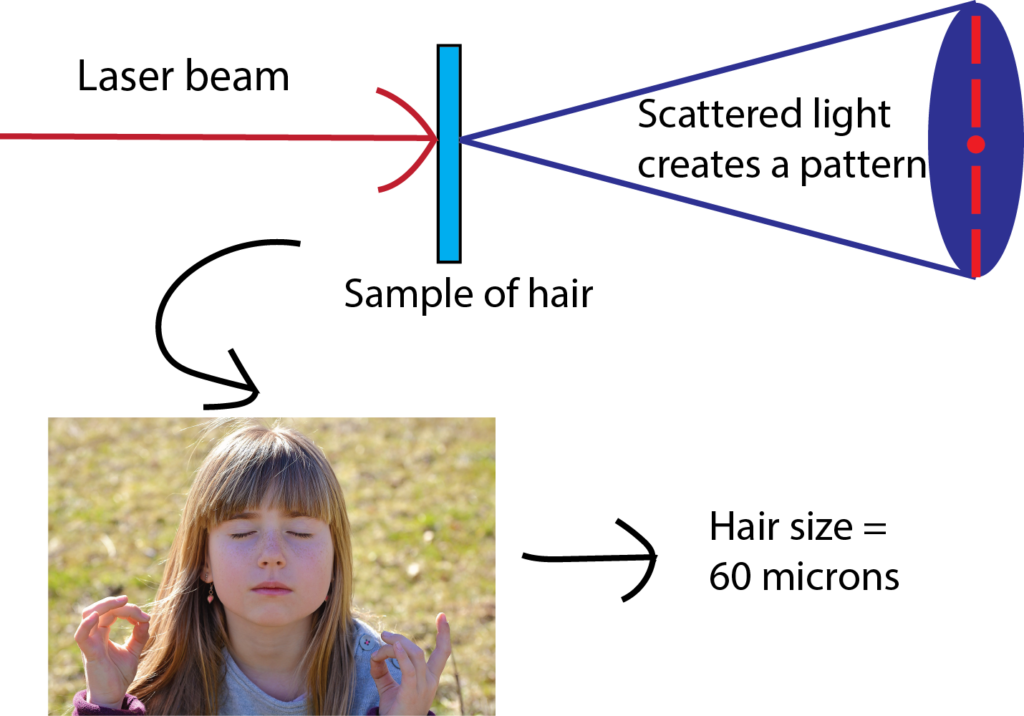
Polymers at Play: Color Me Crystallized!
scallori2025-03-18T19:35:20-06:00How can this ring change color depending on its wearer’s mood? The short answer is polymers—long molecular chains that make up everyday objects like garbage bags and toothbrushes, along with some of your favorite toys! Click to learn how mood rings rely on the shapeshifting behavior of polymers to predict your mood. (Maybe.)