FUNSIZE RESEARCH
Posts showcasing the wonder, beauty, and potential of cutting-edge materials research—freely contributed by physicists from across the country. (Funsize Physics is not responsible for any minds that are blown.)


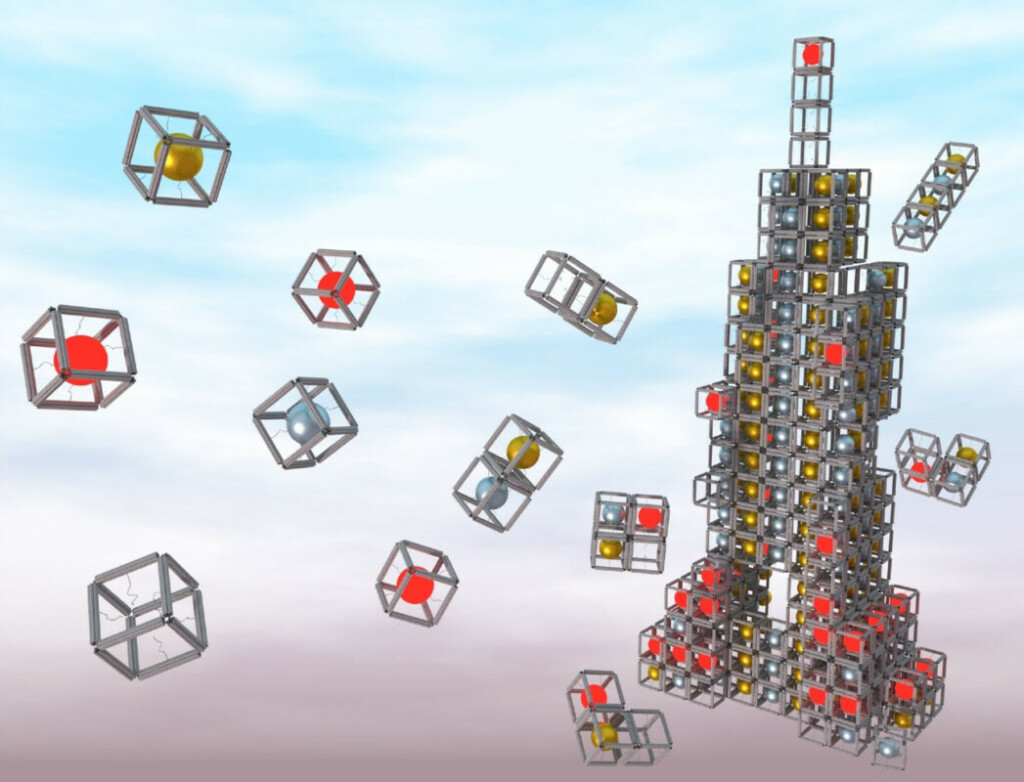
Scientists can use DNA to form nanoblocks of almost any shape and then assemble them into complex three-dimensional structures. Click to explore this fantastic new nanoworld!


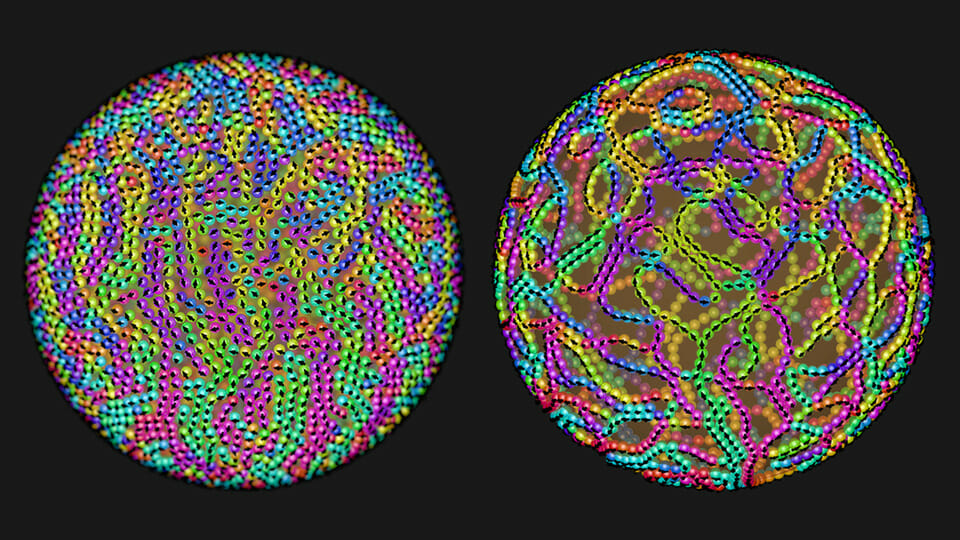
We think we're pretty familiar with how ordinary liquids behave, but it turns out that some of the basic things we know are no longer true when we look at these liquids on short enough length scales and fast enough time scales. The liquids start to behave more like solids, pushing back when you push on them, and slipping across solid surfaces instead of being dragged along. Click to ride the tiny-but-mighty new wave of nanofluidics!


You may have heard that there are three main phases of matter: solids, liquids, and gases (plus plasma if you want to get fancy). Liquids can take virtually any shape and deform instantly. Solid materials possess interesting electronic and magnetic properties essential to our daily life. But how about designing rigid liquids with magnetic properties? Impossible? Not anymore. Click to learn more!


The future of wearable electronics will be smart skins, e-textiles, and other flexible devices. To create these devices, we need new materials that can bend and stretch, but still conduct heat and electricity like traditional metals. Liquid metals to the rescue—read on to learn more!


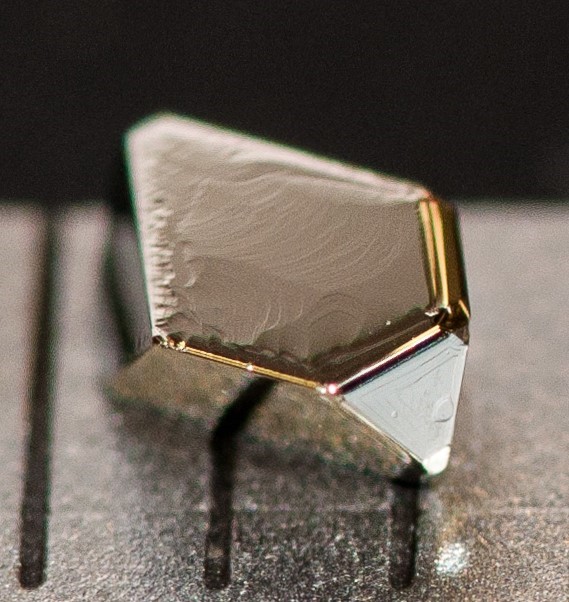
Ferroelectric materials generate electric fields that move charges around, just as a bar magnet produces a magnetic field that moves magnets around. Ferroelectric materials can be used for data storage to make electronics more energy efficient, but they don’t always play well with the silicon technology used in devices like phones and computers. HAFNIA TO THE RESCUE! Click to learn more.


You take a pristine-looking Oreo from a package of seemingly identical sandwich cookies, and you decide to open it up to eat the creme filling first. You gently twist the cookie apart without breaking the chocolate wafers, but the creme sticks to one side only. Why? Happily, the physics of fluids helped two MIT students solve this delicious mystery. Read on to find out what they learned, and how you can test their results at home.


Welcome to the fascinating world of two-dimensional (2D) materials! Today, we're going to explore a novel 2D material created by boiling off atoms, which we guide to form large crystalline flakes that will become the filling in tiny magnetic sandwiches. Intrigued? Click to learn more!


Soap bubbles are marvelously playful. A cascade of bubbles blown into the air can send children running in circles to pop them before they hit the ground. And if you know how to look, soap bubbles are just as playful on much smaller scales, sending scientists running in circles to understand their fascinating physics. Read on to learn more!