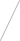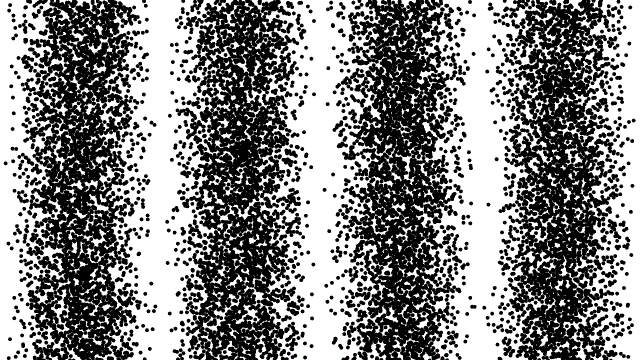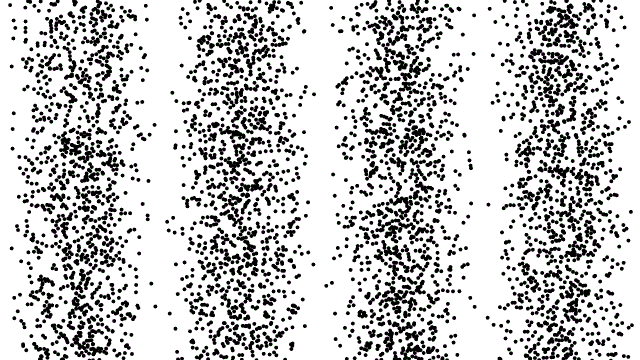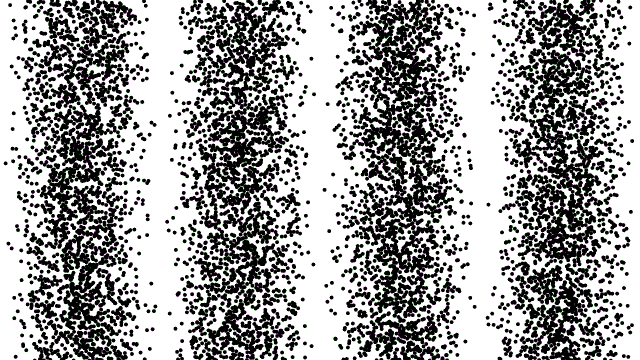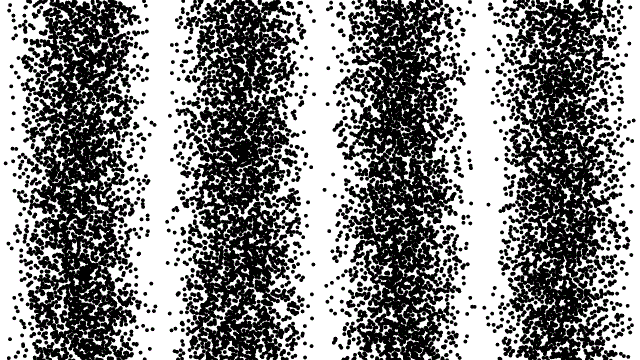FUNSIZE RESEARCH
Posts showcasing the wonder, beauty, and potential of cutting-edge materials research—freely contributed by physicists from across the country. (Funsize Physics is not responsible for any minds that are blown.)


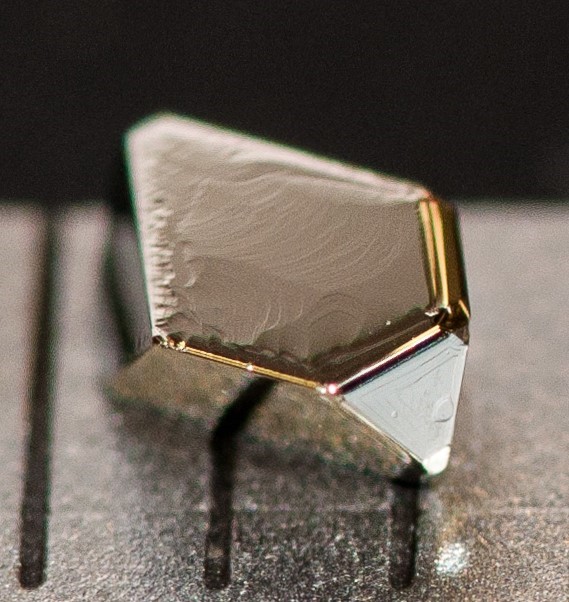
Materials that are absolutely perfect—in other words, materials that contain no defect of any kind—are usually not very interesting. Imagine being married to a saint: you would quickly be bored out of your mind! Defects and impurities can considerably change many properties of materials in ways that allow a wide range of applications.


It’s a hot summer day. You desperately want something cold to drink, but unfortunately, your bottle of root beer has been sitting in a hot car all day. You put it into a bucket full of ice to cool it down. But it’s taking forever! How, you wonder, could you speed the process up? The same question is important for understanding how electronic devices work, and how we can make them work better by controlling the temperature of the electrons that power them. Read on to find out what a bottle of root beer in a cooler full of ice and a nanowire in a vat of liquid helium have in common!


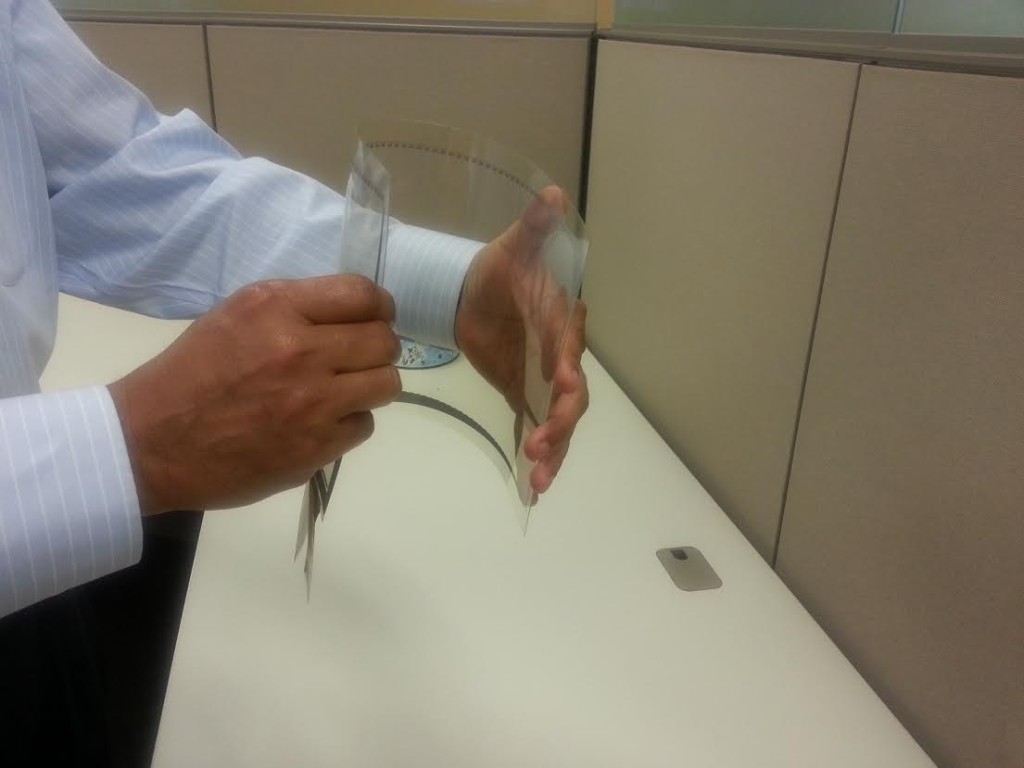
For the past two decades, giant bubble enthusiasts have been creating soap film bubbles of ever-increasing volumes. As of 2020, the world record for a free-floating soap bubble stands at 96.27 cubic meters, a volume equal to about 25,000 U.S. gallons! For a spherical bubble, this corresponds to a diameter of more than 18 feet and a surface area of over 1,000 square feet. How are such large films created and how do they remain stable? What is the secret to giant bubble juice? Click to find out more!


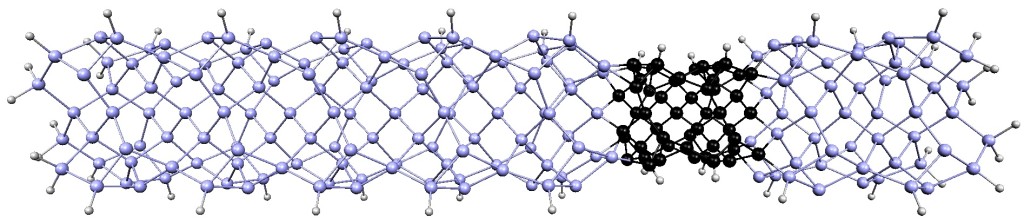
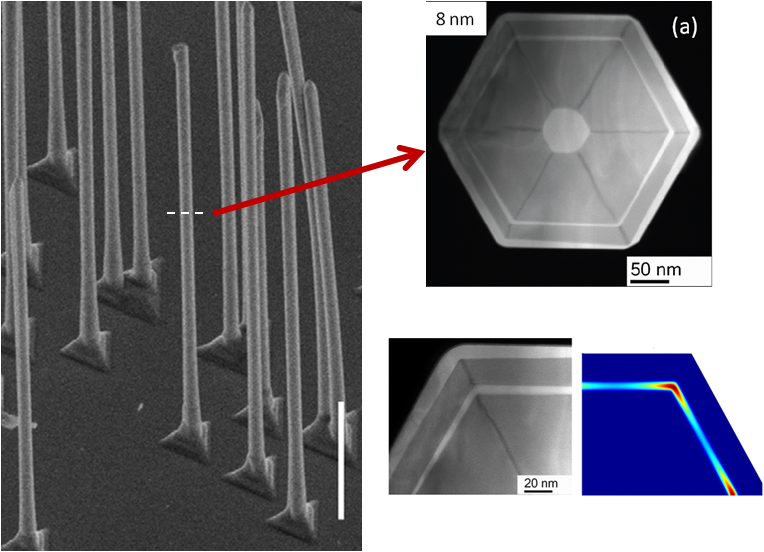
Scientists and engineers are making smaller and smaller structures designed to control the quantum states of electrons in a material. By controlling quantum mechanics, we can create new materials that do not exist in nature, develop more efficient solar cells and faster computer chips, and even discover exotic new states of matter.


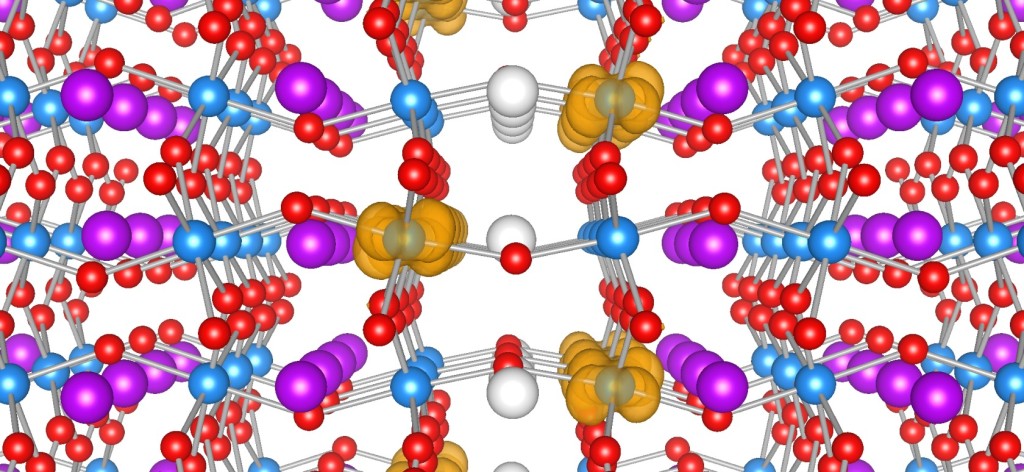
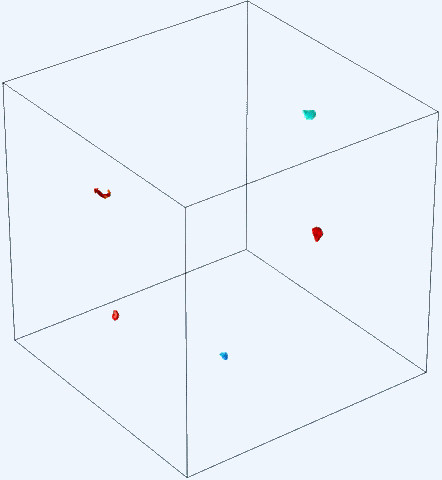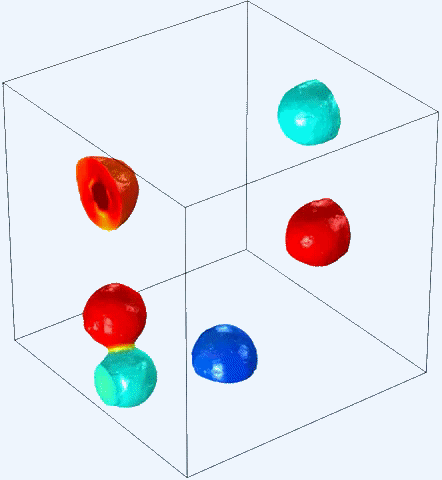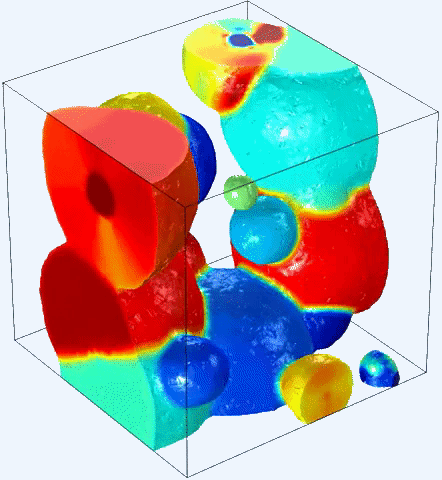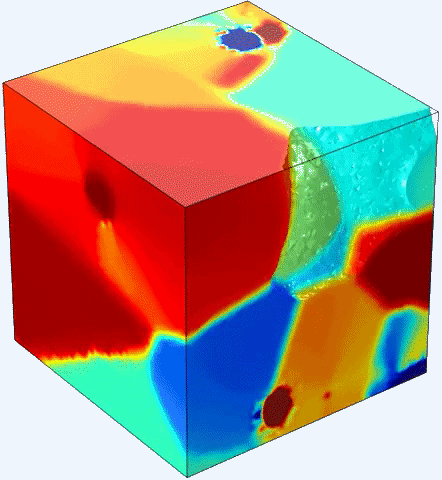
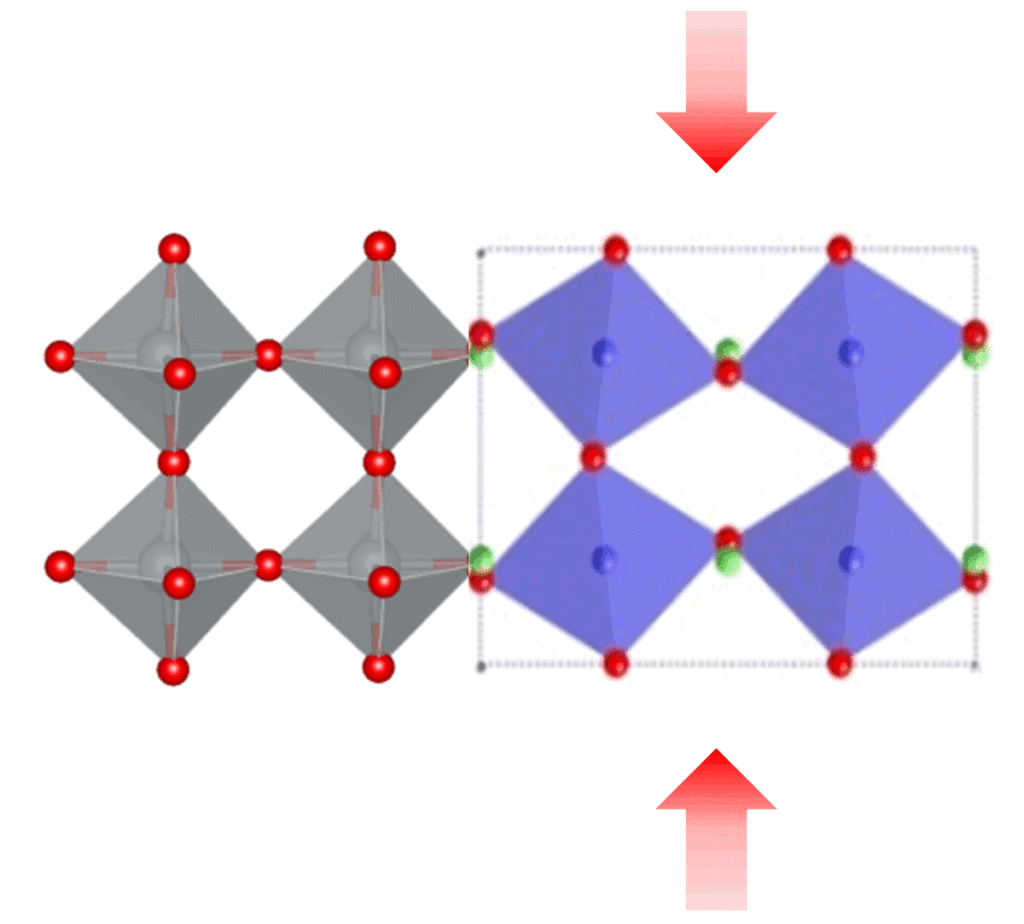
Solids are generally divided into metals, which conduct electricity, and insulators, which do not. Some oxides straddle this boundary, however: a material's structure and properties suggest it should be a metal, but it sometimes behaves as an insulator. Researchers at the University of California, Santa Barbara are digging into the mechanisms of this transformation and are aiming to harness it for use in novel electronic devices.


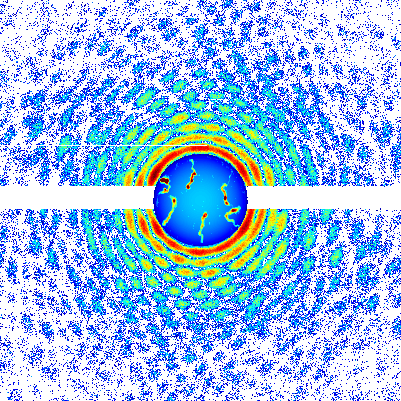
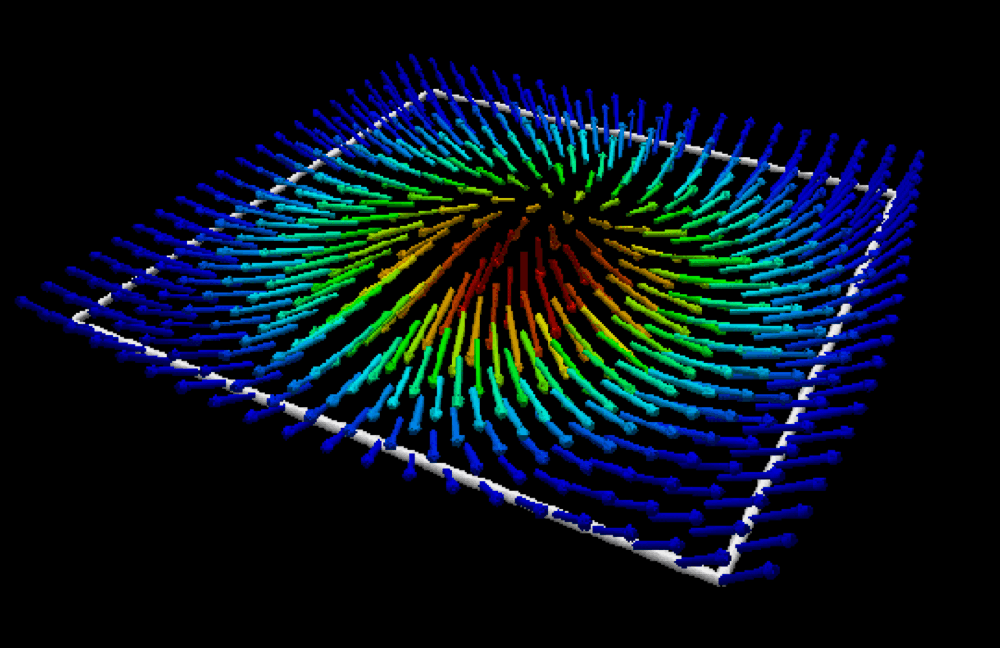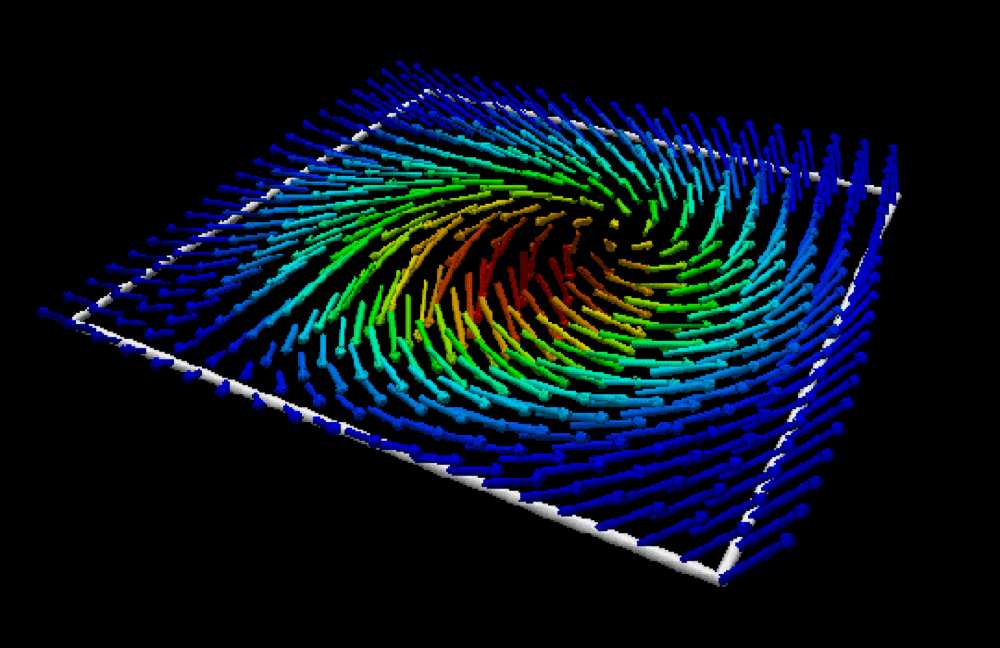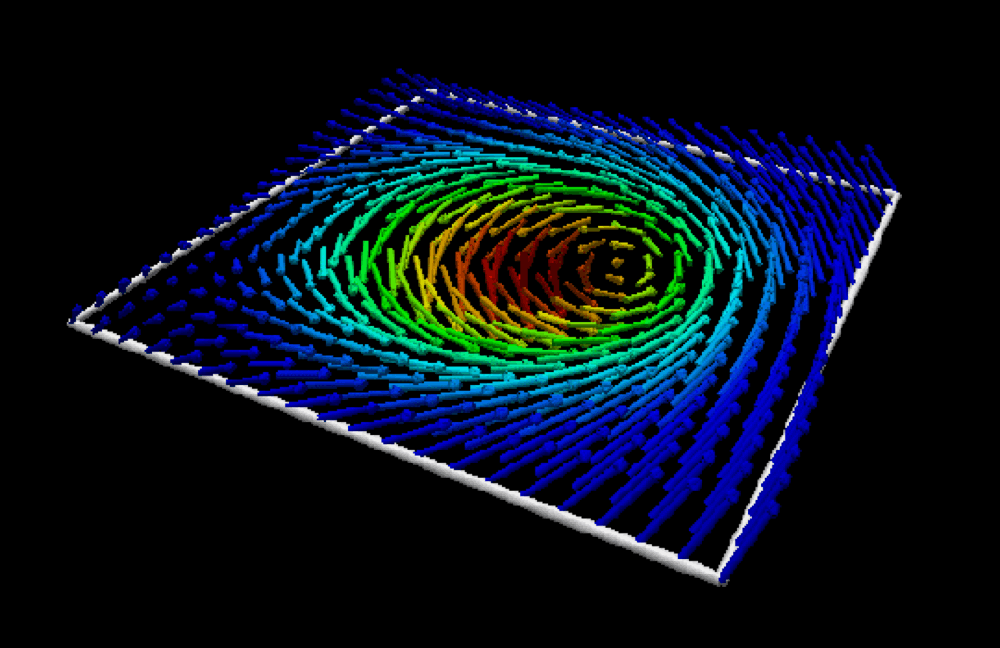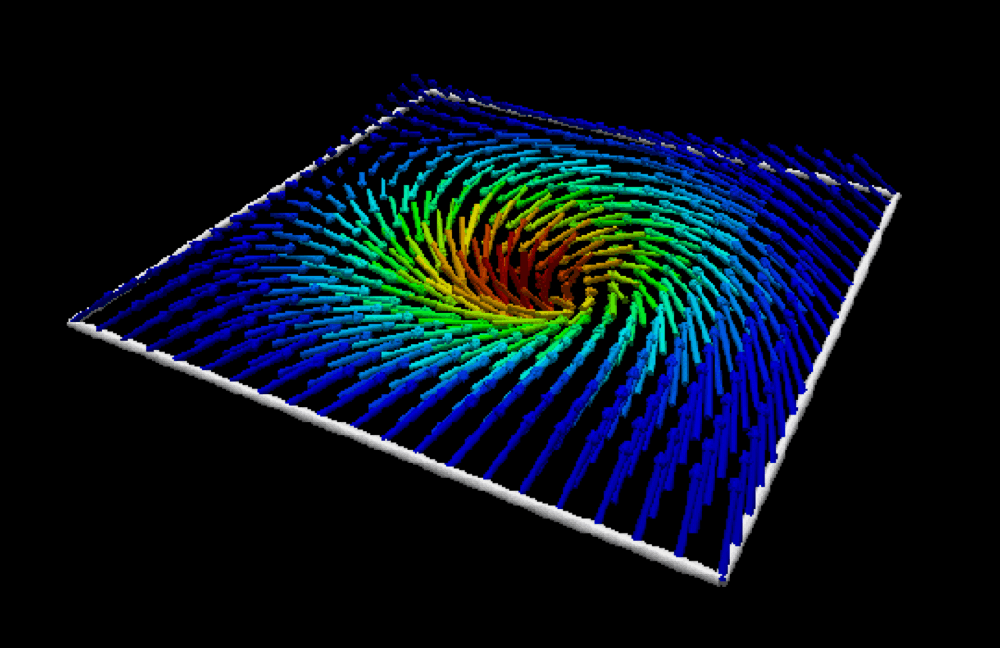
In a unique state of matter called a superfluid, tiny "tornadoes" form that may play an important role in nanotechnology, superconductivity, and other applications. Just as tornadoes are invisible air currents that become visible when they suck debris into their cores, the quantum vortices in superfluids attract atoms that make the vortices visible. Quantum vortices are so small they can only be imaged using very short-wavelength x-rays, however.


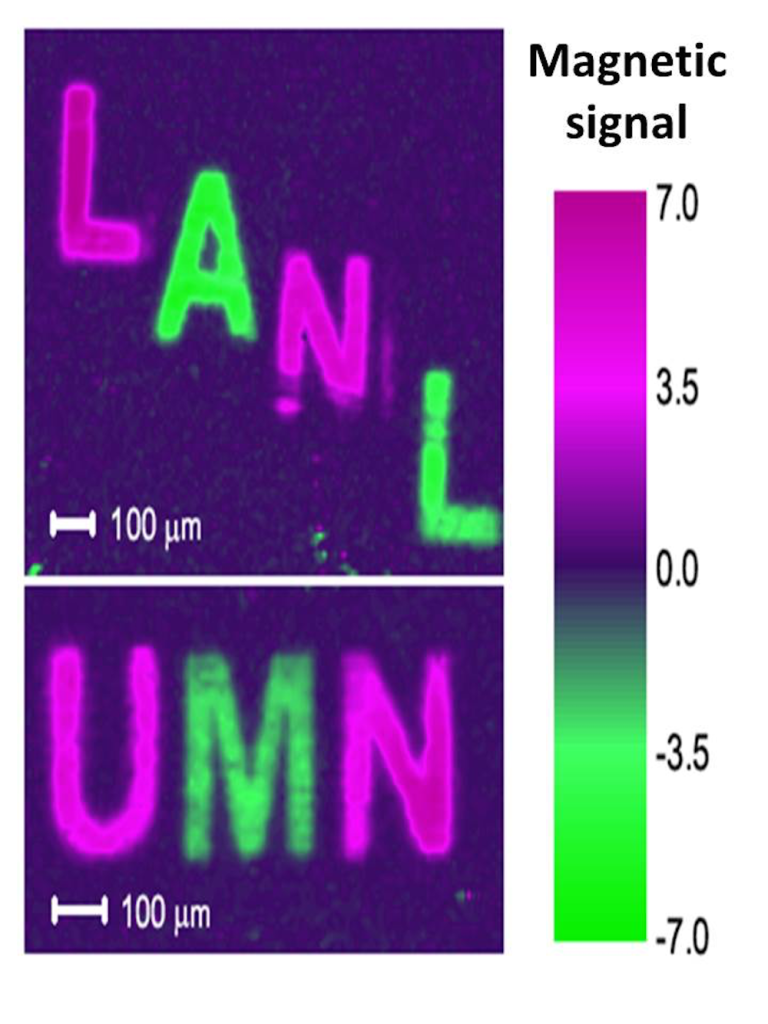
You may know that the media used in magnetic recording technologies, such as computer hard drives, are made of millions of tiny nanomagnets. Each nanomagnet can be switched up or down to record bits of information as ones and zeros. These media are constantly subjected to magnetic fields in order to write, read, and erase information. If you have ever placed a magnet too close to your laptop or cell phone, you know that exposure to an external magnetic field can disrupt information stored this way. Did you know that it is possible for the nanomagnets to "remember" their previous state, if carefully manipulated under specific magnetic field and temperature conditions? Using a kind of memory called topological magnetic memory, scientists have found out how to imprint memory into magnetic thin films by cooling the material under the right conditions.


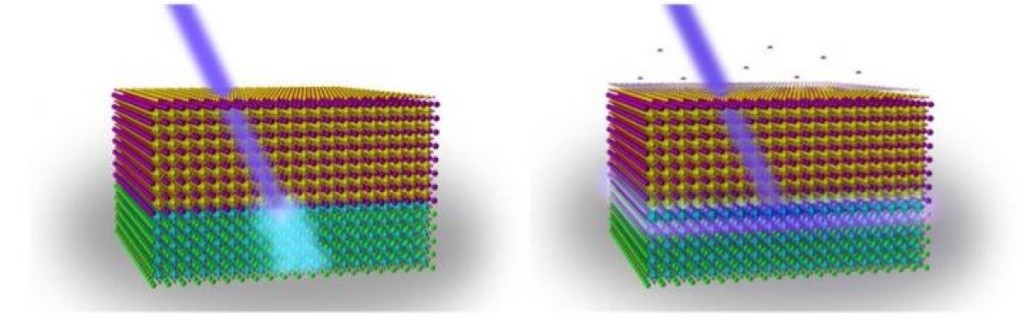
In phase-change memory (PCM), nanoscale volumes of a special kind of glass compound are heated by very short electrical pulses, causing the atomic structure of the material to switch between an ordered phase and a disordered phase. These phase-change materials have been used for years to store data on rewritable CDs and DVDs, but until recently, the large energy required to change the state of the material has made it impractical for electronic memory. If this challenge can be overcome, phase-change memory can be integrated with conventional silicon electronics for high-capacity data storage and more efficient computation. Click to read more about how we are working to make this new technology a reality!


A bit of stray moisture during an experiment tipped off scientists about the strange behavior of a complex oxide material they were studying—shedding light on its potential for improving chemical sensors, computing and information storage. In the presence of a water molecule on its surface, the layered material emits ultraviolet light from its interior.


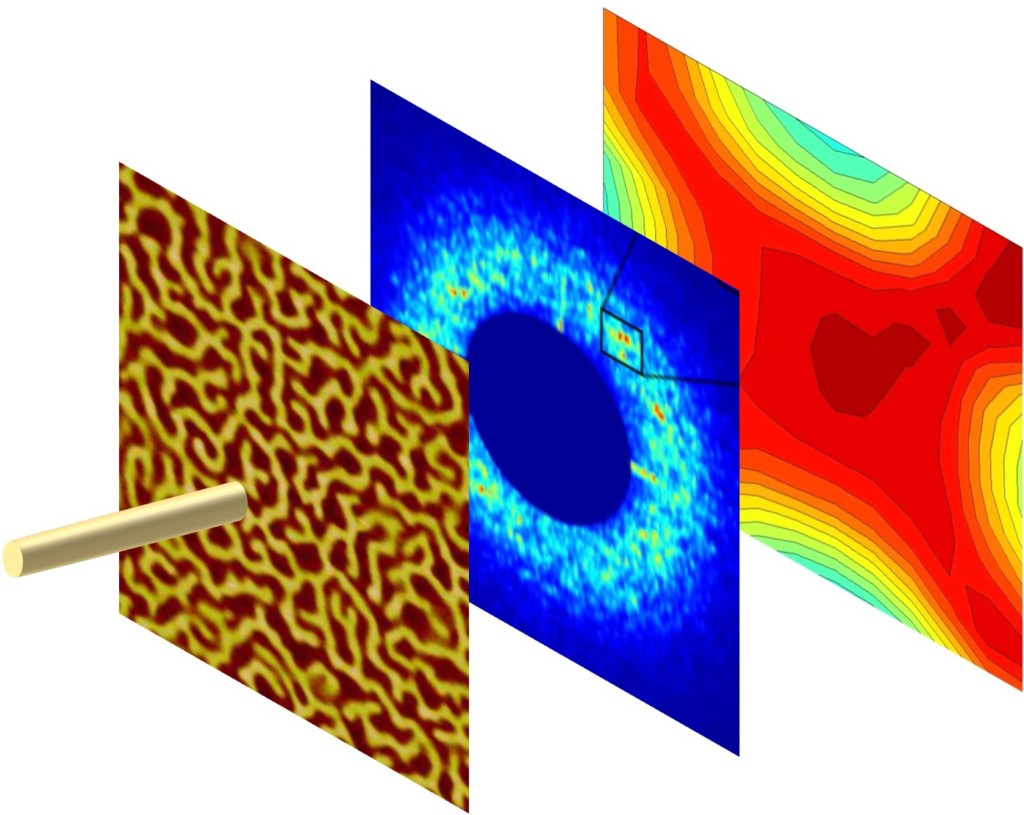
We tend to think of materials as either electrical conductors or insulators: some materials, like metals, have low electrical resistance and conduct electricity easily, while others, like wood or plastic, have high electrical resistance and do not readily conduct electricity. Strange experimental results, however, reveal large fluctuations in the electrical resistance of thin metallic nanowires when a magnetic field or charge difference is applied to them. Click to learn how a more nuanced understanding of electron behavior helps to explain these variations in electrical resistance that may revolutionize the tech industry!


You take a pristine-looking Oreo from a package of seemingly identical sandwich cookies, and you decide to open it up to eat the creme filling first. You gently twist the cookie apart without breaking the chocolate wafers, but the creme sticks to one side only. Why? Happily, the physics of fluids helped two MIT students solve this delicious mystery. Read on to find out what they learned, and how you can test their results at home.


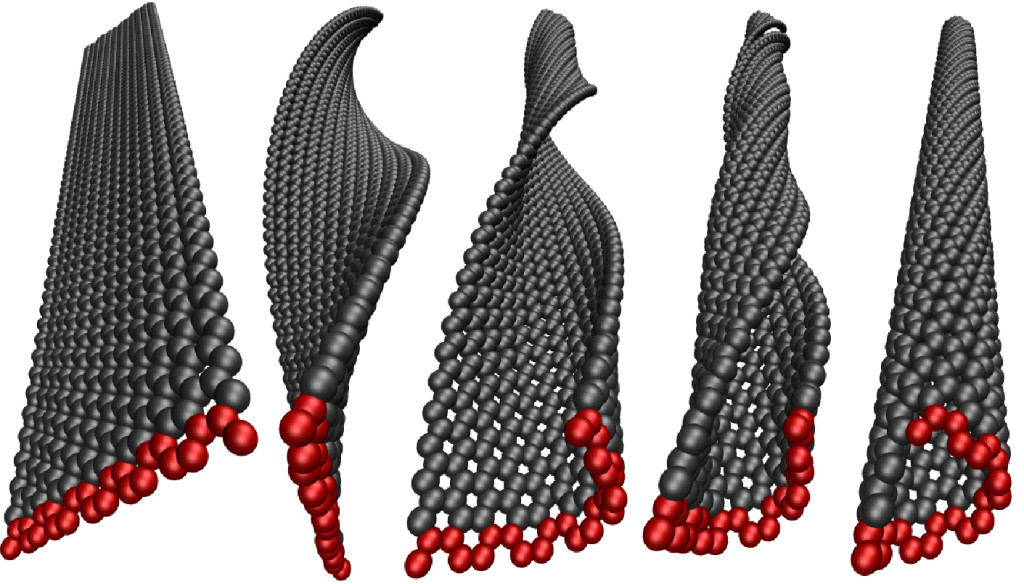
In most magnetic materials, the magnetic moments of individual atoms are aligned parallel to one another and point in the same direction. In special structures called skyrmions and antiskyrmions, however, they are arranged in a spiraling pattern. Their stability and compact size makes skyrmions and antiskyrmions especially useful for encoding lots of data in a small space. But a few questions need to be answered before skyrmion-based technology can be used in your iPhone or other memory devices. First, why do these magnetic structures form in some materials and not others? How can we design a system where they will form? And how can we generate these structures on demand? Click to find out!


Recent progress in materials science has led to the creation of new magnetic materials in which the magnetism follows complex patterns. The formation of these patterns depends on a phenomenon called spin-orbital coupling. Because they can be manipulated by electric currents and temperature changes, materials exhibiting these interesting magnetic patterns may have applications in magnetic memories and logic devices. Click to learn how!


Would you rather have data storage that is compact or reliable? Both, of course! Digital electronic devices like hard drives rely on magnetic memory to store data, encoding information as “0”s and “1”s that correspond to the direction of the magnetic moment, or spin, of atoms in individual bits of material. For magnetic memory to work, the magnetization should not change until the data is erased or rewritten. Unfortunately, some magnetic materials that are promising for high density storage have low data stability, which can be improved by squeezing or stretching the crystal structures of magnetic memory materials, enhancing a material property called magnetic anisotropy.


At low temperatures, helium—the same substance that makes balloons float—becomes a special type of liquid known as a superfluid, which has zero viscosity. It's like the anti-molasses! The properties of superfluids are governed by the laws of quantum mechanics. More specifically, the atoms in superfluid helium are “entangled” with each other, allowing them to share information and influence each other’s behavior in ways that are totally foreign to our everyday experience, and which Einstein famously described as "spooky action at a distance." Better still, scientists have recently discovered that the law controlling entanglement between different parts of a helium superfluid is the same as that governing the exotic behavior of black holes in outer space.